Nightshade Sensitivity and Gut Inflammation: Symptoms and Solutions
Discover how nightshade vegetables may be affecting your digestion and explore natural ways to support your gut health.
What Are Nightshades and Why Do They Affect Gut Health?
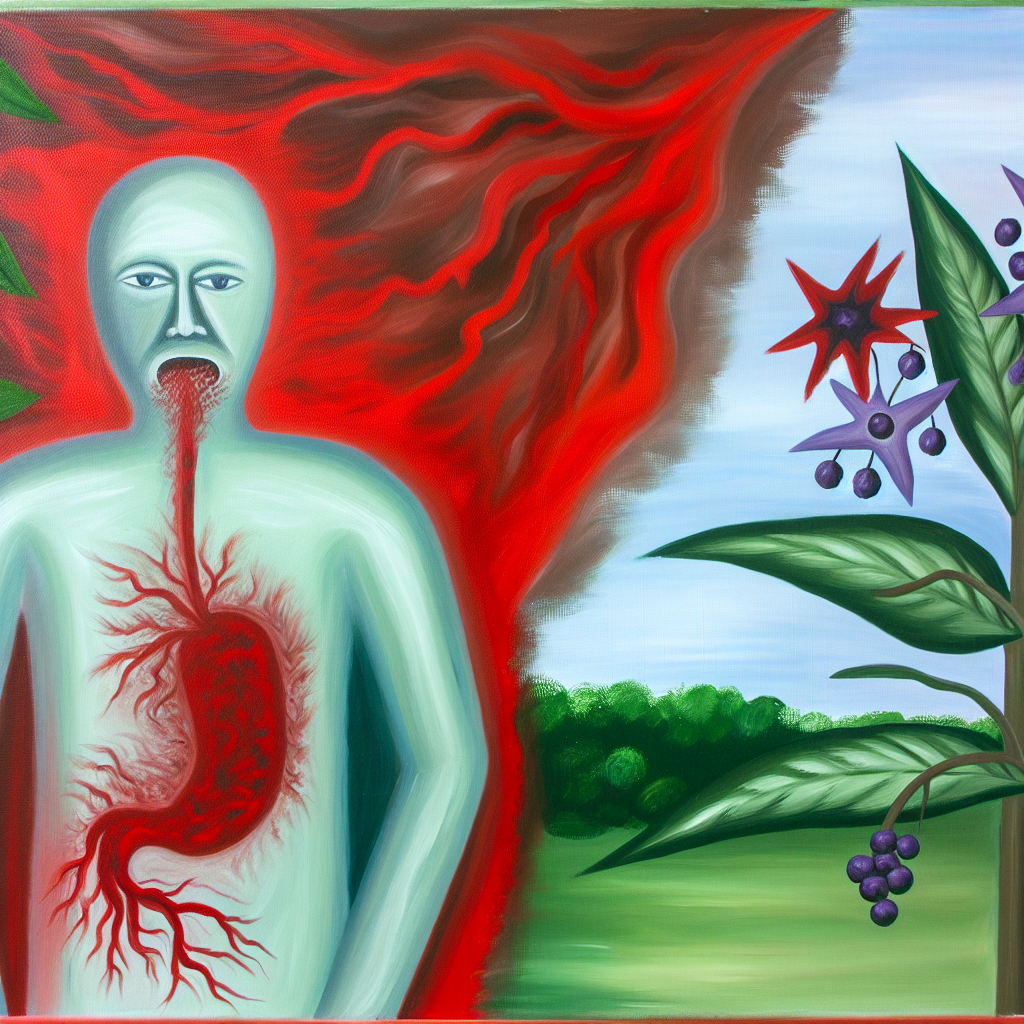
In recent years, awareness surrounding food sensitivities has significantly increased, particularly with the recognition that many individuals struggle with unexplained digestive discomfort. Among the lesser-known culprits contributing to gut health issues are plant compounds known as alkaloids, primarily found in nightshade vegetables. The nightshade family, Solanaceae, includes commonly consumed produce such as tomatoes, potatoes, eggplants, bell peppers, and even goji berries. While nutrient-dense, these foods can be problematic for certain individuals, especially those with autoimmune conditions or existing gut inflammation.
Digestive health is closely tied to the immune system, with over 70% of immune cells residing in the gut mucosa. When this system is compromised, foods that are typically harmless to others can provoke inflammatory responses. In the case of nightshades, their natural chemical compounds—alkaloids like solanine, capsaicin, and tomatine—can become gastrointestinal irritants when consumed in large quantities or when gut integrity is already impaired.
Common Symptoms of Nightshade Sensitivity
Symptoms commonly associated with nightshade sensitivity include:
– Bloating
– Gas
– Diarrhea
– Constipation
– Acid reflux
– Generalized abdominal discomfort
Outside of the gut, individuals may also experience:
– Joint pain
– Fatigue
– Brain fog
– Skin rashes
– Systemic inflammation
Although a true food allergy to nightshades is rare, ongoing sensitivities and intolerances can lead to chronic health problems, particularly for those with conditions such as leaky gut, irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), Crohn’s disease, or other inflammatory bowel disorders.
Scientific Evidence Linking Nightshades to Gut Inflammation
The link between nightshade vegetables and inflammatory responses—especially in the gut—has been widely studied. Glycoalkaloids, particularly solanine and tomatine, are the primary compounds of concern. These naturally occurring chemicals, meant to protect plants from pests, may initiate or worsen inflammation in humans with compromised gut linings.
✅ A key study in the Journal of Autoimmunity (Cordain, 1999) showed that glycoalkaloids can disrupt tight junctions in the gut wall, contributing to increased intestinal permeability or “leaky gut.”
✅ A 2020 observational review found that individuals with rheumatoid arthritis experienced worsened symptoms following nightshade consumption, including joint inflammation and digestive discomfort.
✅ Research published in the journal Nutrients (2019) found that glycoalkaloids may negatively affect beneficial gut bacteria such as Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium, leading to microbiome imbalances and inflammation.
✅ A clinical study in the journal Inflammopharmacology demonstrated improved digestive symptoms and reduced inflammatory markers in participants who followed a 6-week nightshade elimination diet.
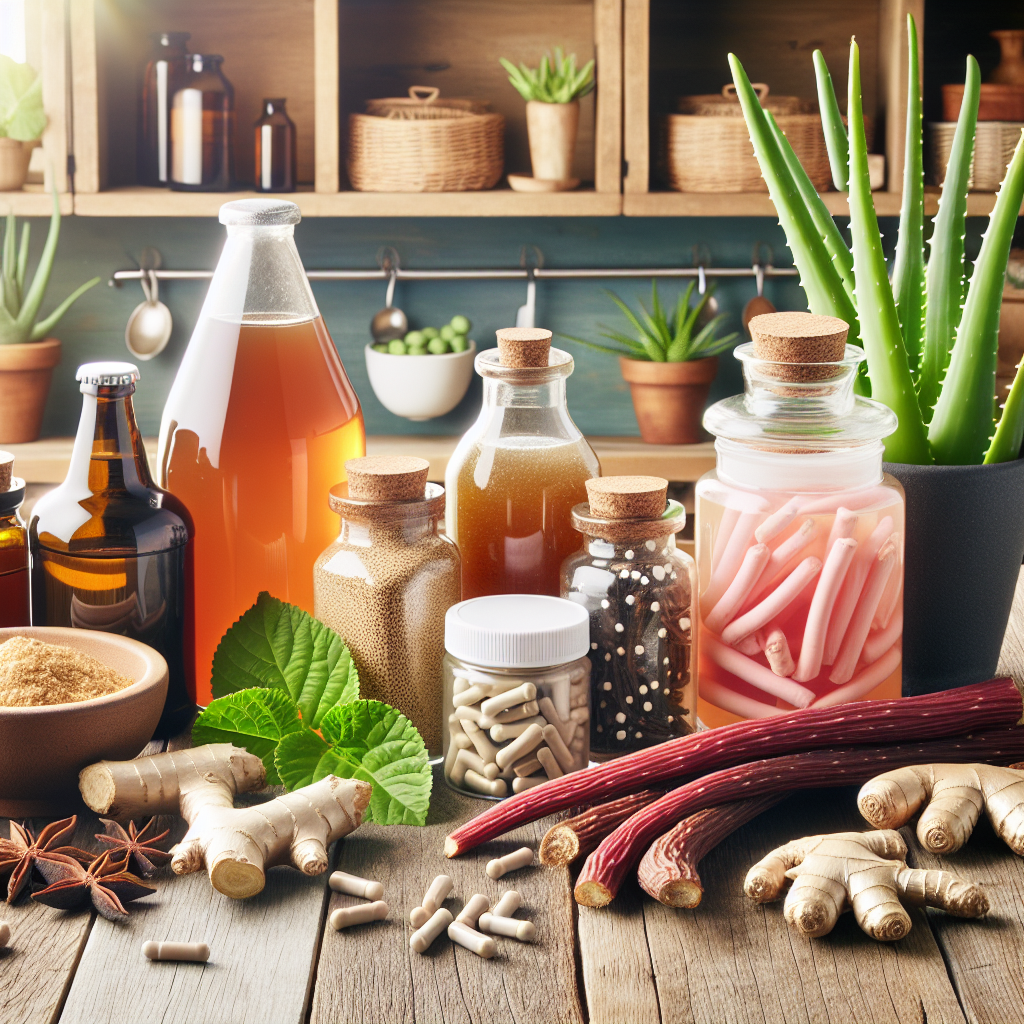
Herbal and Natural Support for Nightshade Sensitivity
Managing nightshade sensitivity naturally often involves a multi-pronged approach. Integrating certain anti-inflammatory and gut-supportive herbs can be highly beneficial:
– 🌿 Turmeric (Curcumin): Potent anti-inflammatory with gut-healing capabilities
– 🌿 Slippery Elm: Coats and soothes the gastrointestinal lining
– 🌿 Deglycyrrhizinated Licorice (DGL): Helps reduce inflammation and heal ulcers
– 🌿 Ginger: Supports digestion and reduces bloating
– 🌿 L-Glutamine: An amino acid that aids in gut mucosa repair and regeneration
These natural tools, alongside mindful dietary changes, can help reduce symptoms and support the gut’s healing process.
How to Identify Nightshade Sensitivity
If you suspect that nightshades are contributing to your digestive symptoms or chronic inflammation, consider these strategies:
1. ✅ Try a 4- to 6-week elimination of all nightshades from your diet.
2. ✅ Reintroduce them one at a time, monitoring symptoms closely.
3. ✅ Keep a food and symptom journal to track reactions.
4. ✅ Work with a functional medicine practitioner or nutritionist to guide your process.
5. ✅ Incorporate gut-healing herbs and supplements during the elimination phase to support recovery.
Conclusion: Listen to Your Gut and Take Control of Your Health
Nightshade sensitivity is an often overlooked but significant contributor to gut inflammation and digestive disorders. While these vegetables offer many nutrients, their glycoalkaloid content can challenge vulnerable digestive and immune systems. By understanding how nightshades affect gut integrity, individuals are empowered to take proactive steps toward healing.
Through elimination diets, targeted reintroductions, and gut-healing protocols, many people have found relief from chronic symptoms. Whether you’re suffering from IBS, autoimmune issues, or persistent bloating, your gut may be telling you it’s time to explore hidden triggers—nightshades included.
With the right awareness, tools, and professional support, it’s possible to restore digestive balance and enjoy lasting wellness.
References
1. Cordain, L., Toohey, L., Smith, M. J., & Hickey, M. S. (1999). Modulation of intestinal permeability by food glycoalkaloids and lectins in disease etiology. Journal of Autoimmunity, 14(3), 247–256. https://doi.org/10.1006/jaut.1999.0297
2. Dietary Glycoalkaloids and Human Health: A Review of Toxicity and Health Benefits. Nutrients. (2019). https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/11/6/1392
3. Nightshades and inflammation: Observational correlations with rheumatoid arthritis symptoms. PubMed Central. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3955101/
4. Elimination diets and their effect on gastrointestinal inflammation: A clinical study. Inflammopharmacology Journal. (2020). https://link.springer.com/journal/10787
5. Healing leaky gut syndrome with natural agents. Alternative Medicine Review. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17217366/
6. The use of curcumin and herbal anti-inflammatories on intestinal health. Evidence-based Complementary and Alternative Medicine. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5664031/
Concise Summary:
Nightshade vegetables, such as tomatoes, potatoes, and peppers, can be problematic for individuals with compromised gut health or autoimmune conditions. The natural compounds in nightshades, called glycoalkaloids, can disrupt the gut lining and contribute to inflammation. Common symptoms of nightshade sensitivity include bloating, gas, and joint pain. By eliminating nightshades and incorporating gut-healing herbs, individuals can find relief from chronic digestive issues and reduce systemic inflammation.

Dominic E. is a passionate filmmaker navigating the exciting intersection of art and science. By day, he delves into the complexities of the human body as a full-time medical writer, meticulously translating intricate medical concepts into accessible and engaging narratives. By night, he explores the boundless realm of cinematic storytelling, crafting narratives that evoke emotion and challenge perspectives.
Film Student and Full-time Medical Writer for ContentVendor.com